ClassLoader源码分析
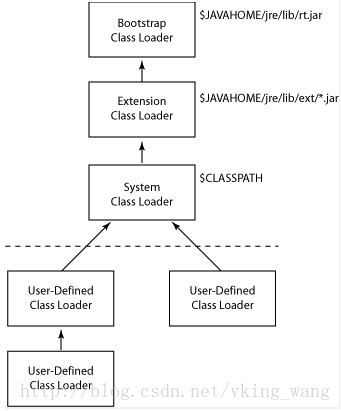
ClassLoader层次结构:
 UML类图:
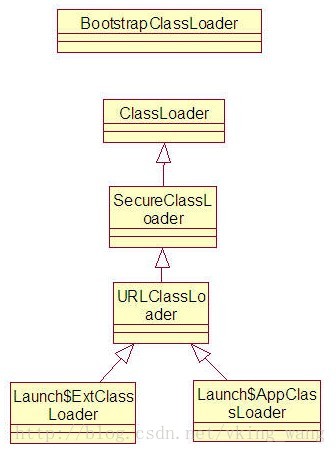
UML类图:
MyClassLoader cl1 = new MyClassLoader();
Class c1 = cl1.findClass("Test.class"); c1.newInstance();
MyClassLoader cl2 = new MyClassLoader();
Class c2 = cl2.findClass("Test.class"); c2.newInstance();
 UML类图:
UML类图:

- sun.misc.Launcher.ExtClassLoader
- sun.misc.Launcher.AppClassLoader
- this.getClass().getClassLoader().loadClass()
- Class.forName()
- MyClassLoader.findClass()
- 调用
findLoadedClass(String)来检查是否已经加载类。 - 在父类加载器上调用
loadClass方法。如果父类加载器为 null,则使用虚拟机的内置类加载器。 - 调用
findClass(String)方法查找类。
public Class<?> loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException { return loadClass(name, false); } /** * Loads the class with the specified <a href="#name">binary name</a>. The * default implementation of this method searches for classes in the * following order: * * <p><ol> * * <li><p> Invoke {@link #findLoadedClass(String)} to check if the class * has already been loaded. </p></li> * * <li><p> Invoke the {@link #loadClass(String) <tt>loadClass</tt>} method * on the parent class loader. If the parent is <tt>null</tt> the class * loader built-in to the virtual machine is used, instead. </p></li> * * <li><p> Invoke the {@link #findClass(String)} method to find the * class. </p></li> * * </ol> * * <p> */ protected synchronized Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException { // First, check if the class has already been loaded Class c = findLoadedClass(name); if (c == null) { try { if (parent != null) { c = parent.loadClass(name, false); } else { c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found // from the non-null parent class loader } if (c == null) { // If still not found, then invoke findClass in order // to find the class. c = findClass(name); } } if (resolve) { resolveClass(c); } return c; }
ClassLoader.loadClass()的最后一步是调用findClass(),这个方法在ClassLoader中并未实现,由其子类负责实现。
findClass()的功能是找到class文件并把字节码加载到内存中。
自定义的ClassLoader一般覆盖这个方法。——以便使用不同的加载路径。
/* The search path for classes and resources */ URLClassPath ucp; /* The context to be used when loading classes and resources */ private AccessControlContext acc; /** * Finds and loads the class with the specified name from the URL search * path. Any URLs referring to JAR files are loaded and opened as needed * until the class is found. * * @param name the name of the class * @return the resulting class * @exception ClassNotFoundException if the class could not be found */ protected Class<?> findClass(final String name) throws ClassNotFoundException { try { return (Class) AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction() { public Object run() throws ClassNotFoundException { String path = name.replace(".", "/").concat(".class"); // 1. URLClassPath ucp,帮助获取class文件字节流 // URLClassPath会用FileLoader或者JarLoader去加载字节码 Resource res = ucp.getResource(path, false); if (res != null) { try { // 2. defineClass,创建类对象,将字节流解析成JVM能够识别的Class对象。 return defineClass(name, res, true); } catch (IOException e) { throw new ClassNotFoundException(name, e); } } else { throw new ClassNotFoundException(name); } } }, acc); } catch (java.security.PrivilegedActionException pae) { throw (ClassNotFoundException) pae.getException(); } } 加载完字节码后,会根据需要进行验证、解析。 /** * Links the specified class. This (misleadingly named) method may be * used by a class loader to link a class. If the class <tt>c</tt> has * already been linked, then this method simply returns. Otherwise, the * class is linked as described in the "Execution" chapter of the <a * href="http://java.sun.com/docs/books/jls/">Java Language Specification</a>. * </p> * * @param c * The class to link * * @throws NullPointerException * If <tt>c</tt> is <tt>null</tt>. * * @see #defineClass(String, byte[], int, int) */ protected final void resolveClass(Class<?> c) { resolveClass0(c); } private native void resolveClass0(Class c);-
findClass()定义加载路径
findClass()的功能是找到class文件并把字节码加载到内存中。
自定义的ClassLoader一般覆盖这个方法。——以便使用不同的加载路径。
在其中调用defineClass()解析字节码。
-
loadClass()定义加载机制
自定义的加载器可以覆盖该方法loadClass(),以便定义不同的加载机制。
例如Servlet中的WebappClassLoader覆盖了该方法,在WEB-INFO/classes目录下查找类文件;在加载时,如果成功,则缓存到ResourceEntry对象。——不同的加载机制。
AppClassLoader覆盖了loadClass()方法。
如果自定义的加载器仅覆盖了findClass,而未覆盖loadClass(即加载规则一样,但加载路径不同);则调用getClass().getClassLoader()返回的仍然是AppClassLoader!因为真正load类的,还是AppClassLoader。
-
实现类的热部署
JVM默认不能热部署类,因为加载类时会去调用findLoadedClass(),如果类已被加载,就不会再次加载。
JVM判断类是否被加载有两个条件:完整类名是否一样、ClassLoader是否是同一个。
所以要实现热部署的话,只需要使用ClassLoader的不同实例来加载。
MyClassLoader cl1 = new MyClassLoader();
Class c1 = cl1.findClass("Test.class"); c1.newInstance();
MyClassLoader cl2 = new MyClassLoader();
Class c2 = cl2.findClass("Test.class"); c2.newInstance();
上例中的c1和c2就是两个不同的实例。
如果用同一个ClassLoader实例来加载,则会抛LinkageError。
-
不可覆盖的final方法
defineClass
/** * Converts an array of bytes into an instance of class <tt>Class</tt>. * Before the <tt>Class</tt> can be used it must be resolved. */ protected final Class<?> defineClass(String name, byte[] b, int off, int len)findLoadedClass
/** * Returns the class with the given <a href="#name">binary name</a> if this * loader has been recorded by the Java virtual machine as an initiating * loader of a class with that <a href="#name">binary name</a>. Otherwise * <tt>null</tt> is returned. </p> */ protected final Class<?> findLoadedClass(String name)findSystemClass
/** * Finds a class with the specified <a href="#name">binary name</a>, * loading it if necessary. * * <p> This method loads the class through the system class loader (see * {@link #getSystemClassLoader()}). The <tt>Class</tt> object returned * might have more than one <tt>ClassLoader</tt> associated with it. * Subclasses of <tt>ClassLoader</tt> need not usually invoke this method, * because most class loaders need to override just {@link #findClass(String)}. </p> */ protected final Class<?> findSystemClass(String name)getParent
/** * Returns the parent class loader for delegation. Some implementations may * use <tt>null</tt> to represent the bootstrap class loader. This method * will return <tt>null</tt> in such implementations if this class loader"s * parent is the bootstrap class loader. */ public final ClassLoader getParent()resolveClass
/** * Links the specified class. This (misleadingly named) method may be * used by a class loader to link a class. If the class <tt>c</tt> has * already been linked, then this method simply returns. Otherwise, the * class is linked as described in the "Execution" chapter of the <a * href="http://java.sun.com/docs/books/jls/">Java Language Specification</a>. */ protected final void resolveClass(Class<?> c)声明:该文观点仅代表作者本人,入门客AI创业平台信息发布平台仅提供信息存储空间服务,如有疑问请联系rumenke@qq.com。
- 上一篇: HashMap实现原理分析
- 下一篇: 【JUnit】EasyMock用法总结

