9、Android与IOS通用AES加密解密方法
1、Android
(1)加密类,Base64Encoder.java
package com.example.aes256;
import java.io.*;
public class Base64Encoder extends FilterOutputStream {
private static final char[] chars = {
"A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "I", "J",
"K", "L", "M", "N", "O", "P", "Q", "R", "S", "T",
"U", "V", "W", "X", "Y", "Z", "a", "b", "c", "d",
"e", "f", "g", "h", "i", "j", "k", "l", "m", "n",
"o", "p", "q", "r", "s", "t", "u", "v", "w", "x",
"y", "z", "0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7",
"8", "9", "+", "/"
};
private int charCount;
private int carryOver;
/***
* Constructs a new Base64 encoder that writes output to the given
* OutputStream.
*
* @param out the output stream
*/
public Base64Encoder(OutputStream out) {
super(out);
}
/***
* Writes the given byte to the output stream in an encoded form.
*
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs
*/
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
// Take 24-bits from three octets, translate into four encoded chars
// Break lines at 76 chars
// If necessary, pad with 0 bits on the right at the end
// Use = signs as padding at the end to ensure encodedLength % 4 == 0
// Remove the sign bit,
// thanks to Christian Schweingruber <chrigu@lorraine.ch>
if (b < 0) {
b += 256;
}
// First byte use first six bits, save last two bits
if (charCount % 3 == 0) {
int lookup = b >> 2;
carryOver = b & 3; // last two bits
out.write(chars[lookup]);
}
// Second byte use previous two bits and first four new bits,
// save last four bits
else if (charCount % 3 == 1) {
int lookup = ((carryOver << 4) + (b >> 4)) & 63;
carryOver = b & 15; // last four bits
out.write(chars[lookup]);
}
// Third byte use previous four bits and first two new bits,
// then use last six new bits
else if (charCount % 3 == 2) {
int lookup = ((carryOver << 2) + (b >> 6)) & 63;
out.write(chars[lookup]);
lookup = b & 63; // last six bits
out.write(chars[lookup]);
carryOver = 0;
}
charCount++;
// Add newline every 76 output chars (that"s 57 input chars)
if (charCount % 57 == 0) {
out.write("
");
}
}
/***
* Writes the given byte array to the output stream in an
* encoded form.
*
* @param buf the data to be written
* @param off the start offset of the data
* @param len the length of the data
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs
*/
public void write(byte[] buf, int off, int len) throws IOException {
// This could of course be optimized
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
write(buf[off + i]);
}
}
/***
* Closes the stream, this MUST be called to ensure proper padding is
* written to the end of the output stream.
*
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs
*/
public void close() throws IOException {
// Handle leftover bytes
if (charCount % 3 == 1) { // one leftover
int lookup = (carryOver << 4) & 63;
out.write(chars[lookup]);
out.write("=");
out.write("=");
}
else if (charCount % 3 == 2) { // two leftovers
int lookup = (carryOver << 2) & 63;
out.write(chars[lookup]);
out.write("=");
}
super.close();
}
/***
* Returns the encoded form of the given unencoded string. The encoder
* uses the ISO-8859-1 (Latin-1) encoding to convert the string to bytes.
* For greater control over the encoding, encode the string to bytes
* yourself and use encode(byte[]).
*
* @param unencoded the string to encode
* @return the encoded form of the unencoded string
*/
public static String encode(String unencoded) {
byte[] bytes = null;
try {
bytes = unencoded.getBytes("UTF-8");
}
catch (UnsupportedEncodingException ignored) { }
return encode(bytes);
}
/***
* Returns the encoded form of the given unencoded string.
*
* @param bytes the bytes to encode
* @return the encoded form of the unencoded string
*/
public static String encode(byte[] bytes) {
ByteArrayOutputStream out =
new ByteArrayOutputStream((int) (bytes.length * 1.37));
Base64Encoder encodedOut = new Base64Encoder(out);
try {
encodedOut.write(bytes);
encodedOut.close();
return out.toString("UTF-8");
}
catch (IOException ignored) { return null; }
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 1) {
System.err.println(
"Usage: java com.oreilly.servlet.Base64Encoder fileToEncode");
return;
}
Base64Encoder encoder = null;
BufferedInputStream in = null;
try {
encoder = new Base64Encoder(System.out);
in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(args[0]));
byte[] buf = new byte[4 * 1024]; // 4K buffer
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = in.read(buf)) != -1) {
encoder.write(buf, 0, bytesRead);
}
}
finally {
if (in != null) in.close();
if (encoder != null) encoder.close();
}
}
}
(2)解密类Base64Decoder.java
package com.example.aes256;
import java.io.*;
public class Base64Decoder extends FilterInputStream {
private static final char[] chars = {
"A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "I", "J",
"K", "L", "M", "N", "O", "P", "Q", "R", "S", "T",
"U", "V", "W", "X", "Y", "Z", "a", "b", "c", "d",
"e", "f", "g", "h", "i", "j", "k", "l", "m", "n",
"o", "p", "q", "r", "s", "t", "u", "v", "w", "x",
"y", "z", "0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7",
"8", "9", "+", "/"
};
// A mapping between char values and six-bit integers
private static final int[] ints = new int[128];
static {
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
ints[chars[i]] = i;
}
}
private int charCount;
private int carryOver;
/***
* Constructs a new Base64 decoder that reads input from the given
* InputStream.
*
* @param in the input stream
*/
public Base64Decoder(InputStream in) {
super(in);
}
/***
* Returns the next decoded character from the stream, or -1 if
* end of stream was reached.
*
* @return the decoded character, or -1 if the end of the
* input stream is reached
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs
*/
public int read() throws IOException {
// Read the next non-whitespace character
int x;
do {
x = in.read();
if (x == -1) {
return -1;
}
} while (Character.isWhitespace((char)x));
charCount++;
// The "=" sign is just padding
if (x == "=") {
return -1; // effective end of stream
}
// Convert from raw form to 6-bit form
x = ints[x];
// Calculate which character we"re decoding now
int mode = (charCount - 1) % 4;
// First char save all six bits, go for another
if (mode == 0) {
carryOver = x & 63;
return read();
}
// Second char use previous six bits and first two new bits,
// save last four bits
else if (mode == 1) {
int decoded = ((carryOver << 2) + (x >> 4)) & 255;
carryOver = x & 15;
return decoded;
}
// Third char use previous four bits and first four new bits,
// save last two bits
else if (mode == 2) {
int decoded = ((carryOver << 4) + (x >> 2)) & 255;
carryOver = x & 3;
return decoded;
}
// Fourth char use previous two bits and all six new bits
else if (mode == 3) {
int decoded = ((carryOver << 6) + x) & 255;
return decoded;
}
return -1; // can"t actually reach this line
}
/***
* Reads decoded data into an array of bytes and returns the actual
* number of bytes read, or -1 if end of stream was reached.
*
* @param buf the buffer into which the data is read
* @param off the start offset of the data
* @param len the maximum number of bytes to read
* @return the actual number of bytes read, or -1 if the end of the
* input stream is reached
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs
*/
public int read(byte[] buf, int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (buf.length < (len + off - 1)) {
throw new IOException("The input buffer is too small: " + len +
" bytes requested starting at offset " + off + " while the buffer " +
" is only " + buf.length + " bytes long.");
}
// This could of course be optimized
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int x = read();
if (x == -1 && i == 0) { // an immediate -1 returns -1
return -1;
}
else if (x == -1) { // a later -1 returns the chars read so far
break;
}
buf[off + i] = (byte) x;
}
return i;
}
/***
* Returns the decoded form of the given encoded string, as a String.
* Note that not all binary data can be represented as a String, so this
* method should only be used for encoded String data. Use decodeToBytes()
* otherwise.
*
* @param encoded the string to decode
* @return the decoded form of the encoded string
*/
public static String decode(String encoded) {
return new String(decodeToBytes(encoded));
}
/***
* Returns the decoded form of the given encoded string, as bytes.
*
* @param encoded the string to decode
* @return the decoded form of the encoded string
*/
public static byte[] decodeToBytes(String encoded) {
byte[] bytes = null;
try {
bytes = encoded.getBytes("UTF-8");
}
catch (UnsupportedEncodingException ignored) { }
Base64Decoder in = new Base64Decoder(
new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
ByteArrayOutputStream out =
new ByteArrayOutputStream((int) (bytes.length * 0.67));
try {
byte[] buf = new byte[4 * 1024]; // 4K buffer
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = in.read(buf)) != -1) {
out.write(buf, 0, bytesRead);
}
out.close();
return out.toByteArray();
}
catch (IOException ignored) { return null; }
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 1) {
System.err.println("Usage: java Base64Decoder fileToDecode");
return;
}
Base64Decoder decoder = null;
try {
decoder = new Base64Decoder(
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(args[0])));
byte[] buf = new byte[4 * 1024]; // 4K buffer
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = decoder.read(buf)) != -1) {
System.out.write(buf, 0, bytesRead);
}
}
finally {
if (decoder != null) decoder.close();
}
}
}
(3)封装类,AES.java。用于调用加密解密类
package com.example.aes256;
/**
* LICENSE AND TRADEMARK NOTICES
*
* Except where noted, sample source code written by Motorola Mobility Inc. and
* provided to you is licensed as described below.
*
* Copyright (c) 2012, Motorola, Inc.
* All rights reserved except as otherwise explicitly indicated.
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
*
* - Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
* this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
*
* - Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
* this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
* and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
*
* - Neither the name of Motorola, Inc. nor the names of its contributors may
* be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without
* specific prior written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
* AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
* IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
* ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE
* LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
* CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF
* SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS
* INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN
* CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE)
* ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Other source code displayed may be licensed under Apache License, Version
* 2.
*
* Copyright © 2012, Android Open Source Project. All rights reserved unless
* otherwise explicitly indicated.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not
* use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy
* of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT
* WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the
* License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations
* under the License.
*
*/
// Please refer to the accompanying article at
// http://developer.motorola.com/docs/using_the_advanced_encryption_standard_in_android/
// A tutorial guide to using AES encryption in Android
// First we generate a 256 bit secret key; then we use that secret key to AES encrypt a plaintext message.
// Finally we decrypt the ciphertext to get our original message back.
// We don"t keep a copy of the secret key - we generate the secret key whenever it is needed,
// so we must remember all the parameters needed to generate it -
// the salt, the IV, the human-friendly passphrase, all the algorithms and parameters to those algorithms.
// Peter van der Linden, April 15 2012
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.security.InvalidAlgorithmParameterException;
import java.security.InvalidKeyException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.spec.InvalidKeySpecException;
import javax.crypto.BadPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException;
import javax.crypto.NoSuchPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.SecretKeyFactory;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.PBEKeySpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import android.util.Log;
public class AES {
// private final String KEY_GENERATION_ALG = "PBEWITHSHAANDTWOFISH-CBC";
private final String KEY_GENERATION_ALG = "PBKDF2WithHmacSHA1";
private final int HASH_ITERATIONS = 10000;
private final int KEY_LENGTH = 256;
private char[] humanPassphrase = { "P", "e", "r", " ", "v", "a", "l", "l",
"u", "m", " ", "d", "u", "c", "e", "s", " ", "L", "a", "b", "a",
"n", "t" };
// char[] humanPassphrase = { "v", "t", "i", "o", "n","s","f","o","t", ".",
// "c", "o", "m",
// "p"};
private byte[] salt = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0xA, 0xB, 0xC, 0xD,
0xE, 0xF }; // must save this for next time we want the key
private PBEKeySpec myKeyspec = new PBEKeySpec(humanPassphrase, salt,
HASH_ITERATIONS, KEY_LENGTH);
private final String CIPHERMODEPADDING = "AES/CBC/PKCS7Padding";
private SecretKeyFactory keyfactory = null;
private SecretKey sk = null;
private SecretKeySpec skforAES = null;
private byte[] iv = { 0xA, 1, 0xB, 5, 4, 0xF, 7, 9, 0x17, 3, 1, 6, 8, 0xC,
0xD, 91 };
private IvParameterSpec IV;
public AES() {
try {
keyfactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_GENERATION_ALG);
sk = keyfactory.generateSecret(myKeyspec);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException nsae) {
Log.e("AESdemo",
"no key factory support for PBEWITHSHAANDTWOFISH-CBC");
} catch (InvalidKeySpecException ikse) {
Log.e("AESdemo", "invalid key spec for PBEWITHSHAANDTWOFISH-CBC");
}
// This is our secret key. We could just save this to a file instead of
// regenerating it
// each time it is needed. But that file cannot be on the device (too
// insecure). It could
// be secure if we kept it on a server accessible through https.
byte[] skAsByteArray = sk.getEncoded();
// Log.d("",
// "skAsByteArray=" + skAsByteArray.length + ","
// + Base64Encoder.encode(skAsByteArray));
skforAES = new SecretKeySpec(skAsByteArray, "AES");
;
IV = new IvParameterSpec(iv);
}
public String encrypt(byte[] plaintext) {
byte[] ciphertext = encrypt(CIPHERMODEPADDING, skforAES, IV, plaintext);
String base64_ciphertext = Base64Encoder.encode(ciphertext);
return base64_ciphertext;
}
public String decrypt(String ciphertext_base64) {
byte[] s = Base64Decoder.decodeToBytes(ciphertext_base64);
String decrypted = new String(decrypt(CIPHERMODEPADDING, skforAES, IV,
s));
return decrypted;
}
// Use this method if you want to add the padding manually
// AES deals with messages in blocks of 16 bytes.
// This method looks at the length of the message, and adds bytes at the end
// so that the entire message is a multiple of 16 bytes.
// the padding is a series of bytes, each set to the total bytes added (a
// number in range 1..16).
private byte[] addPadding(byte[] plain) {
byte plainpad[] = null;
int shortage = 16 - (plain.length % 16);
// if already an exact multiple of 16, need to add another block of 16
// bytes
if (shortage == 0)
shortage = 16;
// reallocate array bigger to be exact multiple, adding shortage bits.
plainpad = new byte[plain.length + shortage];
for (int i = 0; i < plain.length; i++) {
plainpad[i] = plain[i];
}
for (int i = plain.length; i < plain.length + shortage; i++) {
plainpad[i] = (byte) shortage;
}
return plainpad;
}
// Use this method if you want to remove the padding manually
// This method removes the padding bytes
private byte[] dropPadding(byte[] plainpad) {
byte plain[] = null;
int drop = plainpad[plainpad.length - 1]; // last byte gives number of
// bytes to drop
// reallocate array smaller, dropping the pad bytes.
plain = new byte[plainpad.length - drop];
for (int i = 0; i < plain.length; i++) {
plain[i] = plainpad[i];
plainpad[i] = 0; // don"t keep a copy of the decrypt
}
return plain;
}
private byte[] encrypt(String cmp, SecretKey sk, IvParameterSpec IV,
byte[] msg) {
try {
Cipher c = Cipher.getInstance(cmp);
c.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, sk, IV);
return c.doFinal(msg);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException nsae) {
Log.e("AESdemo", "no cipher getinstance support for " + cmp);
} catch (NoSuchPaddingException nspe) {
Log.e("AESdemo", "no cipher getinstance support for padding " + cmp);
} catch (InvalidKeyException e) {
Log.e("AESdemo", "invalid key exception");
} catch (InvalidAlgorithmParameterException e) {
Log.e("AESdemo", "invalid algorithm parameter exception");
} catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) {
Log.e("AESdemo", "illegal block size exception");
} catch (BadPaddingException e) {
Log.e("AESdemo", "bad padding exception");
}
return null;
}
private byte[] decrypt(String cmp, SecretKey sk, IvParameterSpec IV,
byte[] ciphertext) {
try {
Cipher c = Cipher.getInstance(cmp);
c.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, sk, IV);
return c.doFinal(ciphertext);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException nsae) {
Log.e("AESdemo", "no cipher getinstance support for " + cmp);
} catch (NoSuchPaddingException nspe) {
Log.e("AESdemo", "no cipher getinstance support for padding " + cmp);
} catch (InvalidKeyException e) {
Log.e("AESdemo", "invalid key exception");
} catch (InvalidAlgorithmParameterException e) {
Log.e("AESdemo", "invalid algorithm parameter exception");
} catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) {
Log.e("AESdemo", "illegal block size exception");
} catch (BadPaddingException e) {
Log.e("AESdemo", "bad padding exception");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
(4)使用类
package com.example.aes256;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.YuvImage;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
AES gAes = new AES();
String sendString="欢迎,Hello World!";
byte[] sendBytes = null;
try {
sendBytes = sendString .getBytes("UTF8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
String str = gAes.encrypt(sendBytes);
System.out.println(str);
String result = gAes.decrypt(str);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
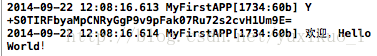
(5)结果

2、IOS
(1)加密解密类
NSData+AES256.h#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import <CommonCrypto/CommonCryptor.h> #import <CommonCrypto/CommonKeyDerivation.h> @interface NSData (AES256) + (NSString *)AES256EncryptWithPlainText:(NSString *)plain; /*加密方法,参数需要加密的内容*/ + (NSString *)AES256DecryptWithCiphertext:(NSString *)ciphertexts; /*解密方法,参数数密文*/ @endNSData+AES256.m
//
// NSData+AES256.m
// AES
//
// Created by Henry Yu on 2009/06/03.
// Copyright 2010 Sevensoft Technology Co., Ltd.(http://www.sevenuc.com)
// All rights reserved.
//
// Permission is given to use this source code file, free of charge, in any
// project, commercial or otherwise, entirely at your risk, with the condition
// that any redistribution (in part or whole) of source code must retain
// this copyright and permission notice. Attribution in compiled projects is
// appreciated but not required.
//
#import "NSData+AES256.h"
#define PASSWORD @"Per vallum duces Labant"
static const char encodingTable[] = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/";
const NSUInteger kAlgorithmKeySize = kCCKeySizeAES256;
const NSUInteger kPBKDFRounds = 10000; // ~80ms on an iPhone 4
static Byte saltBuff[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0xA,0xB,0xC,0xD,0xE,0xF};
static Byte ivBuff[] = {0xA,1,0xB,5,4,0xF,7,9,0x17,3,1,6,8,0xC,0xD,91};
@implementation NSData (AES256)
+ (NSData *)AESKeyForPassword:(NSString *)password{ //Derive a key from a text password/passphrase
NSMutableData *derivedKey = [NSMutableData dataWithLength:kAlgorithmKeySize];
NSData *salt = [NSData dataWithBytes:saltBuff length:kCCKeySizeAES128];
int result = CCKeyDerivationPBKDF(kCCPBKDF2, // algorithm算法
password.UTF8String, // password密码
password.length, // passwordLength密码的长度
salt.bytes, // salt内容
salt.length, // saltLen长度
kCCPRFHmacAlgSHA1, // PRF
kPBKDFRounds, // rounds循环次数
derivedKey.mutableBytes, // derivedKey
derivedKey.length); // derivedKeyLen derive:出自
NSAssert(result == kCCSuccess,
@"Unable to create AES key for spassword: %d", result);
return derivedKey;
}
/*加密方法*/
+ (NSString *)AES256EncryptWithPlainText:(NSString *)plain {
NSData *plainText = [plain dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
// "key" should be 32 bytes for AES256, will be null-padded otherwise
char keyPtr[kCCKeySizeAES256+1]; // room for terminator (unused)
bzero(keyPtr, sizeof(keyPtr)); // fill with zeroes (for padding)
NSUInteger dataLength = [plainText length];
size_t bufferSize = dataLength + kCCBlockSizeAES128;
void *buffer = malloc(bufferSize);
bzero(buffer, sizeof(buffer));
size_t numBytesEncrypted = 0;
CCCryptorStatus cryptStatus = CCCrypt(kCCEncrypt, kCCAlgorithmAES128,kCCOptionPKCS7Padding,
[[NSData AESKeyForPassword:PASSWORD] bytes], kCCKeySizeAES256,
ivBuff /* initialization vector (optional) */,
[plainText bytes], dataLength, /* input */
buffer, bufferSize, /* output */
&numBytesEncrypted);
if (cryptStatus == kCCSuccess) {
NSData *encryptData = [NSData dataWithBytesNoCopy:buffer length:numBytesEncrypted];
return [encryptData base64Encoding];
}
free(buffer); //free the buffer;
return nil;
}
/*解密方法*/
+ (NSString *)AES256DecryptWithCiphertext:(NSString *)ciphertexts{
NSData *cipherData = [NSData dataWithBase64EncodedString:ciphertexts];
// "key" should be 32 bytes for AES256, will be null-padded otherwise
char keyPtr[kCCKeySizeAES256+1]; // room for terminator (unused)
bzero(keyPtr, sizeof(keyPtr)); // fill with zeroes (for padding)
NSUInteger dataLength = [cipherData length];
size_t bufferSize = dataLength + kCCBlockSizeAES128;
void *buffer = malloc(bufferSize);
size_t numBytesDecrypted = 0;
CCCryptorStatus cryptStatus = CCCrypt(kCCDecrypt, kCCAlgorithmAES128, kCCOptionPKCS7Padding,
[[NSData AESKeyForPassword:PASSWORD] bytes], kCCKeySizeAES256,
ivBuff ,/* initialization vector (optional) */
[cipherData bytes], dataLength, /* input */
buffer, bufferSize, /* output */
&numBytesDecrypted);
if (cryptStatus == kCCSuccess) {
NSData *encryptData = [NSData dataWithBytesNoCopy:buffer length:numBytesDecrypted];
return [[[NSString alloc] initWithData:encryptData encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding] init];
}
free(buffer); //free the buffer;
return nil;
}
+ (id)dataWithBase64EncodedString:(NSString *)string;
{
if (string == nil)
[NSException raise:NSInvalidArgumentException format:nil];
if ([string length] == 0)
return [NSData data];
static char *decodingTable = NULL;
if (decodingTable == NULL)
{
decodingTable = malloc(256);
if (decodingTable == NULL)
return nil;
memset(decodingTable, CHAR_MAX, 256);
NSUInteger i;
for (i = 0; i < 64; i++)
decodingTable[(short)encodingTable[i]] = i;
}
const char *characters = [string cStringUsingEncoding:NSASCIIStringEncoding];
if (characters == NULL) // Not an ASCII string!
return nil;
char *bytes = malloc((([string length] + 3) / 4) * 3);
if (bytes == NULL)
return nil;
NSUInteger length = 0;
NSUInteger i = 0;
while (YES)
{
char buffer[4];
short bufferLength;
for (bufferLength = 0; bufferLength < 4; i++)
{
if (characters[i] == "�")
break;
if (isspace(characters[i]) || characters[i] == "=")
continue;
buffer[bufferLength] = decodingTable[(short)characters[i]];
if (buffer[bufferLength++] == CHAR_MAX) // Illegal character!
{
free(bytes);
return nil;
}
}
if (bufferLength == 0)
break;
if (bufferLength == 1) // At least two characters are needed to produce one byte!
{
free(bytes);
return nil;
}
// Decode the characters in the buffer to bytes.
bytes[length++] = (buffer[0] << 2) | (buffer[1] >> 4);
if (bufferLength > 2)
bytes[length++] = (buffer[1] << 4) | (buffer[2] >> 2);
if (bufferLength > 3)
bytes[length++] = (buffer[2] << 6) | buffer[3];
}
bytes = realloc(bytes, length);
return [NSData dataWithBytesNoCopy:bytes length:length];
}
- (NSString *)base64Encoding;
{
if ([self length] == 0)
return @"";
char *characters = malloc((([self length] + 2) / 3) * 4);
if (characters == NULL)
return nil;
NSUInteger length = 0;
NSUInteger i = 0;
while (i < [self length])
{
char buffer[3] = {0,0,0};
short bufferLength = 0;
while (bufferLength < 3 && i < [self length])
buffer[bufferLength++] = ((char *)[self bytes])[i++];
// Encode the bytes in the buffer to four characters, including padding "=" characters if necessary.
characters[length++] = encodingTable[(buffer[0] & 0xFC) >> 2];
characters[length++] = encodingTable[((buffer[0] & 0x03) << 4) | ((buffer[1] & 0xF0) >> 4)];
if (bufferLength > 1)
characters[length++] = encodingTable[((buffer[1] & 0x0F) << 2) | ((buffer[2] & 0xC0) >> 6)];
else characters[length++] = "=";
if (bufferLength > 2)
characters[length++] = encodingTable[buffer[2] & 0x3F];
else characters[length++] = "=";
}
return [[[NSString alloc] initWithBytesNoCopy:characters length:length encoding:NSASCIIStringEncoding freeWhenDone:YES] init];
}
@end
(2)使用
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
NSString* message = @"欢迎,Hello World!";
NSString* str = [NSData AES256EncryptWithPlainText:message];
NSString* res = [NSData AES256DecryptWithCiphertext:str];
NSLog(@"%@",str);
NSLog(@"%@",res);
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
}
(3)结果
声明:该文观点仅代表作者本人,入门客AI创业平台信息发布平台仅提供信息存储空间服务,如有疑问请联系rumenke@qq.com。
- 上一篇:没有了
- 下一篇: NGUI实现UISprite拼接

